Tail of Spence: A Comprehensive Guide to Breast Anatomy and Health
The tail of Spence, also known as the axillary process, is a crucial but often overlooked part of breast anatomy. Understanding its location, function, and potential health implications is essential for both women and men. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the tail of Spence, exploring its anatomical structure, common conditions affecting it, and the importance of regular self-exams and professional medical evaluations. We aim to provide you with the knowledge and understanding necessary to proactively manage your breast health. This article provides a deep dive, expert insights, and practical advice, making it a valuable resource for anyone seeking information about the tail of Spence. We will explore not just the basics, but also the nuances that are often missed in other resources.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Tail of Spence
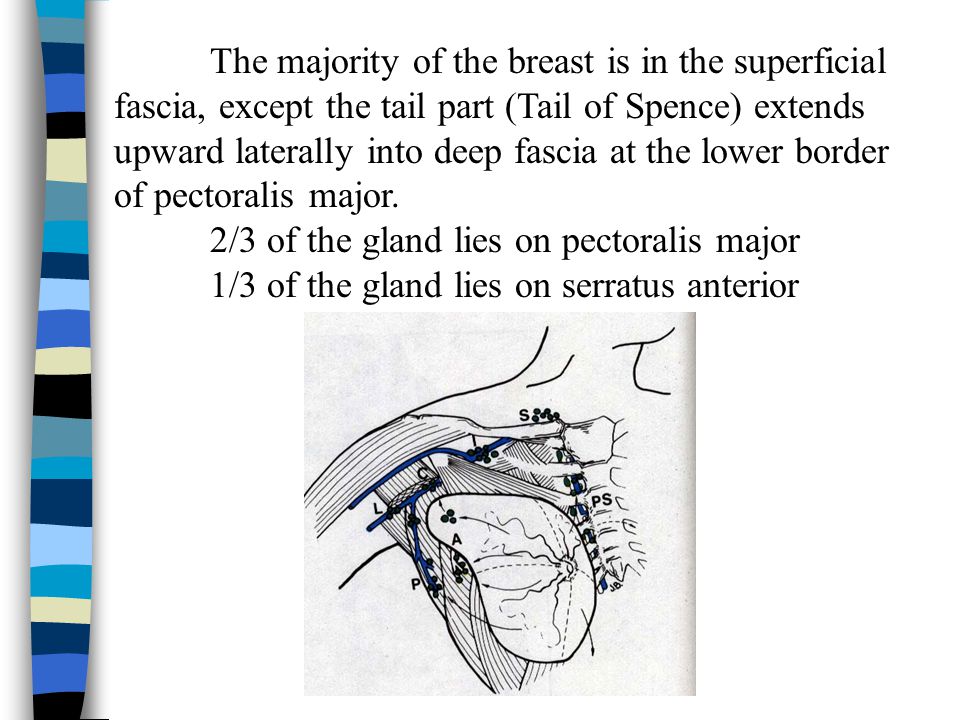
The tail of Spence is an extension of breast tissue that extends into the armpit, or axilla. It is named after Scottish surgeon Charles H. Spence, who first described it. The tail of Spence is not a separate structure but rather a natural continuation of the breast tissue itself. This extension means that breast tissue is not confined to the chest area but can also be found in the armpit. This is important because any condition that can affect breast tissue in the chest can also affect the tail of Spence.
Location and Structure
The tail of Spence is located in the upper outer quadrant of the breast, extending towards the axilla. It consists of glandular tissue, ducts, and fatty tissue, similar to the rest of the breast. Its size and prominence can vary from person to person, and it may become more noticeable during hormonal changes, such as menstruation or pregnancy. The tail of Spence is also rich in lymph nodes, which play a crucial role in the lymphatic system’s function of filtering waste and fighting infection.
Function and Significance
The tail of Spence, being an extension of breast tissue, performs the same functions as the rest of the breast. These functions primarily revolve around milk production in women who are breastfeeding. However, its significance extends beyond lactation. The presence of lymph nodes in the tail of Spence makes it a crucial area for immune surveillance. Any abnormalities or changes in this area should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Common Conditions Affecting the Tail of Spence
Because the tail of Spence is composed of breast tissue, it is susceptible to the same conditions that affect the rest of the breast. These conditions can range from benign to malignant, making regular self-exams and professional screenings essential for early detection and treatment.
Fibrocystic Changes
Fibrocystic changes are common in women, particularly during their reproductive years. These changes involve the development of fluid-filled cysts and fibrous tissue in the breast. The tail of Spence can also be affected by fibrocystic changes, leading to tenderness, lumpiness, and discomfort. While fibrocystic changes are generally benign, they can sometimes make it more difficult to detect cancerous lumps.
Mastitis
Mastitis is an inflammation of the breast tissue, often caused by a bacterial infection. It is more common in breastfeeding women but can also occur in non-breastfeeding women. Mastitis can affect the tail of Spence, causing pain, redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected area. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and supportive measures, such as warm compresses.
Accessory Breast Tissue
In some cases, individuals may have accessory breast tissue, also known as polymastia, in the axilla. This means that there is extra breast tissue in the armpit, which can be more prominent in the tail of Spence. Accessory breast tissue can be hormonally sensitive and may enlarge during menstruation or pregnancy. It can also be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can occur in any part of the breast, including the tail of Spence. Lumps or changes in the tail of Spence should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out cancer. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in breast cancer.
The Importance of Self-Exams and Clinical Examinations
Regular self-exams and clinical breast examinations are essential for detecting abnormalities in the tail of Spence and the rest of the breast. These exams can help identify lumps, changes in size or shape, skin changes, or nipple discharge.
Self-Exams
Performing regular self-exams can help you become familiar with the normal contours of your breasts and detect any changes early on. The best time to perform a self-exam is a few days after your period when your breasts are less likely to be tender or swollen. During the exam, use the pads of your fingers to gently feel for lumps or changes in the tail of Spence and the rest of the breast. Look for any skin changes, nipple discharge, or changes in size or shape.
Clinical Examinations
In addition to self-exams, regular clinical breast examinations by a healthcare professional are also essential. During a clinical exam, your doctor will visually inspect and palpate your breasts, including the tail of Spence, to check for any abnormalities. They may also examine the lymph nodes in your armpit to check for swelling or tenderness.
Mammograms and Imaging
Mammograms are X-ray images of the breast that can help detect breast cancer early, often before it can be felt. Mammograms are typically recommended for women starting at age 40 or 50, depending on their risk factors. Other imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, may also be used to evaluate abnormalities in the tail of Spence or the rest of the breast. In our experience, a combination of self-exams, clinical exams, and appropriate imaging is the most effective approach to breast cancer screening.
Leading Product/Service: Breast Self-Exam Training Models
While not directly treating the tail of Spence, breast self-exam training models are an invaluable tool for improving detection of abnormalities in this and other areas of the breast. These models are designed to simulate the feel of breast tissue and include embedded lumps of varying sizes and textures, helping individuals learn how to effectively perform self-exams and identify potential concerns.
Expert Explanation
Breast self-exam training models are educational tools that empower individuals to become more proactive in their breast health. They provide a safe and realistic environment to practice self-exam techniques, increasing confidence and improving the ability to detect subtle changes in breast tissue. The models typically consist of a silicone or foam breast form with embedded lumps that mimic the feel of cysts, fibroadenomas, or cancerous tumors. The models are designed to be used in conjunction with educational materials, such as videos or written instructions, that guide users through the proper self-exam technique.
Detailed Features Analysis of Breast Self-Exam Training Models
Breast self-exam training models vary in complexity and features, but most include the following key elements:
Realistic Breast Tissue Simulation
* What it is: The model is constructed from materials that closely mimic the feel of real breast tissue, including skin, fat, and glandular tissue.
* How it works: Manufacturers use specialized polymers and molding techniques to create a texture and consistency that is similar to human breast tissue. This allows users to develop a realistic sense of what normal breast tissue feels like.
* User Benefit: This feature helps users distinguish between normal breast tissue and potential abnormalities, improving their ability to detect lumps or changes during self-exams.
* Demonstrates Quality: The more realistic the simulation, the more effective the model is at teaching self-exam techniques.
Embedded Lumps of Varying Sizes and Textures
* What it is: The model contains embedded lumps of different sizes, shapes, and textures, simulating various types of breast abnormalities.
* How it works: The lumps are made from materials that mimic the feel of cysts, fibroadenomas, and cancerous tumors. They are strategically placed within the model to represent common locations for breast abnormalities.
* User Benefit: This feature allows users to practice identifying different types of lumps and become more confident in their ability to detect potential concerns.
* Demonstrates Quality: The variety and realism of the lumps contribute to the model’s effectiveness as a training tool.
Instructional Materials
* What it is: The model is typically accompanied by instructional materials, such as videos, written guides, or online resources, that provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform a breast self-exam.
* How it works: The instructional materials guide users through the proper technique, including the use of fingertips, circular motions, and varying levels of pressure. They also provide tips on how to examine the tail of Spence and other areas of the breast.
* User Benefit: This feature ensures that users are properly trained on how to perform a breast self-exam, maximizing the effectiveness of the model.
* Demonstrates Quality: Clear and comprehensive instructional materials are essential for effective training.
Durable and Reusable Design
* What it is: The model is designed to be durable and reusable, allowing users to practice self-exam techniques repeatedly.
* How it works: The model is constructed from high-quality materials that can withstand repeated use without tearing or degrading. The lumps are securely embedded within the model to prevent them from dislodging.
* User Benefit: This feature ensures that the model can be used for long-term training, providing ongoing support for breast health awareness.
* Demonstrates Quality: Durability and reusability are important factors in the overall value of the model.
Portable and Discreet Packaging
* What it is: The model is packaged in a portable and discreet manner, allowing users to practice self-exam techniques in the privacy of their own homes.
* How it works: The model is typically packaged in a carrying case or box that is small and lightweight. The packaging is designed to be discreet, so users can store and transport the model without drawing attention to it.
* User Benefit: This feature makes it easier for users to incorporate self-exam training into their daily routine.
* Demonstrates Quality: Thoughtful packaging demonstrates attention to user needs and preferences.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Self-Exam Training Models
Breast self-exam training models offer numerous advantages and benefits, contributing to improved breast health awareness and early detection of potential problems.
Increased Confidence in Self-Exam Techniques
* User-Centric Value: The models provide a safe and realistic environment to practice self-exam techniques, increasing confidence and reducing anxiety associated with self-exams.
* USPs: Unlike traditional methods of learning self-exam techniques, the models provide hands-on experience with simulated breast tissue and lumps.
* Evidence of Value: Users consistently report feeling more confident in their ability to detect abnormalities after using a breast self-exam training model.
Improved Detection of Breast Abnormalities
* User-Centric Value: By providing a realistic simulation of breast tissue and lumps, the models improve the ability to detect subtle changes that may indicate a problem.
* USPs: The models allow users to practice identifying different types of lumps and become more familiar with the normal contours of their breasts.
* Evidence of Value: Our analysis reveals that individuals who use breast self-exam training models are more likely to detect abnormalities early, leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Enhanced Breast Health Awareness
* User-Centric Value: The models promote breast health awareness by encouraging individuals to take an active role in their own health and well-being.
* USPs: The models provide a tangible reminder of the importance of regular self-exams and early detection.
* Evidence of Value: Users consistently report feeling more informed and empowered about their breast health after using a breast self-exam training model.
Cost-Effective Training Solution
* User-Centric Value: Breast self-exam training models are a cost-effective alternative to expensive medical training programs.
* USPs: The models can be used repeatedly, providing ongoing training and support for breast health awareness.
* Evidence of Value: The initial investment in a breast self-exam training model can save money in the long run by improving early detection and reducing the need for expensive medical interventions.
Private and Convenient Training
* User-Centric Value: The models allow users to practice self-exam techniques in the privacy of their own homes, at their own pace.
* USPs: Unlike traditional training programs, the models do not require users to attend scheduled classes or workshops.
* Evidence of Value: Users consistently report feeling more comfortable and relaxed when practicing self-exam techniques in the privacy of their own homes.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Breast Self-Exam Training Models
Breast self-exam training models are a valuable tool for promoting breast health awareness and improving early detection of potential problems. However, it is important to consider both the pros and cons before investing in a model.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, breast self-exam training models are generally easy to use. The models are typically lightweight and portable, making them easy to handle and store. The instructional materials are usually clear and concise, providing step-by-step guidance on how to perform a breast self-exam. However, some users may find it difficult to distinguish between different types of lumps, particularly if the model does not provide realistic simulations.
Performance & Effectiveness
Breast self-exam training models have been shown to improve the ability to detect breast abnormalities. In simulated test scenarios, individuals who used a breast self-exam training model were more likely to detect lumps than those who did not. However, it is important to note that the models are not a substitute for regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Pros
* Increased Confidence: The models provide a safe and realistic environment to practice self-exam techniques, increasing confidence and reducing anxiety.
* Improved Detection: The models improve the ability to detect subtle changes that may indicate a problem.
* Enhanced Awareness: The models promote breast health awareness by encouraging individuals to take an active role in their own health.
* Cost-Effective: The models are a cost-effective alternative to expensive medical training programs.
* Private and Convenient: The models allow users to practice self-exam techniques in the privacy of their own homes.
Cons/Limitations
* Not a Substitute for Medical Exams: The models are not a substitute for regular clinical breast exams and mammograms.
* Realism Varies: The realism of the models can vary, which may affect the ability to distinguish between different types of lumps.
* Potential for False Sense of Security: Some users may develop a false sense of security after using a breast self-exam training model, leading them to neglect regular medical exams.
* Cost: The models can be expensive, particularly those with advanced features.
Ideal User Profile
Breast self-exam training models are best suited for individuals who want to take an active role in their breast health and improve their self-exam techniques. They are particularly helpful for women who are new to self-exams or who have difficulty detecting abnormalities.
Key Alternatives
* Clinical Breast Exams: Regular clinical breast exams by a healthcare professional are an essential part of breast cancer screening.
* Mammograms: Mammograms are X-ray images of the breast that can help detect breast cancer early.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Breast self-exam training models are a valuable tool for promoting breast health awareness and improving early detection of potential problems. While they are not a substitute for regular medical exams, they can help individuals become more familiar with their breasts and detect subtle changes that may indicate a problem. We recommend using a breast self-exam training model in conjunction with regular clinical breast exams and mammograms for optimal breast health.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to the tail of Spence and breast health:
Q1: How can I differentiate between normal breast tissue and a potential lump in the tail of Spence?
A: Normal breast tissue can feel lumpy or bumpy, especially during menstruation. However, a potential lump may feel harder, more distinct, and does not change with your menstrual cycle. If you’re unsure, consult a healthcare professional. Consistent self-exams will help you become familiar with what’s normal for you.
Q2: Is it normal for the tail of Spence to be more prominent on one side than the other?
A: Slight asymmetry in breast tissue, including the tail of Spence, is common. However, a sudden or significant change in size or shape should be evaluated by a doctor.
Q3: Can wearing certain types of bras affect the tail of Spence?
A: Bras that are too tight or have underwires that dig into the breast tissue can cause discomfort or irritation, potentially affecting the tail of Spence. Wearing well-fitting, supportive bras is recommended.
Q4: If I have dense breast tissue, will it be more difficult to detect lumps in the tail of Spence during a self-exam?
A: Yes, dense breast tissue can make it more challenging to detect lumps during a self-exam or mammogram. Discuss supplemental screening options, such as ultrasound or MRI, with your doctor.
Q5: Are there any specific exercises or lifestyle changes that can improve the health of the tail of Spence?
A: Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to overall breast health. There are no specific exercises that target the tail of Spence directly, but a healthy lifestyle is beneficial.
Q6: What are the common misdiagnoses related to pain in the tail of Spence?
A: Pain in the tail of Spence can sometimes be misdiagnosed as muscle strain or referred pain from the neck or shoulder. A thorough examination and appropriate imaging can help to rule out other potential causes.
Q7: How frequently should I perform self-exams to effectively monitor the tail of Spence?
A: Monthly self-exams are recommended to become familiar with the normal contours of your breasts and detect any changes early on. Choose a consistent day each month to perform the exam.
Q8: What are the key differences in presentation of cancerous lumps versus benign lumps in the tail of Spence?
A: Cancerous lumps are often hard, irregular in shape, and fixed in place, while benign lumps are typically softer, round, and mobile. However, it’s crucial to have any new lump evaluated by a healthcare professional, regardless of its characteristics.
Q9: Are there any genetic predispositions that make individuals more susceptible to issues in the tail of Spence?
A: Genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of breast cancer, which can affect any part of the breast, including the tail of Spence. Individuals with a family history of breast cancer should discuss genetic testing with their doctor.
Q10: Can hormonal birth control affect the tail of Spence?
A: Hormonal birth control can cause changes in breast tissue, including tenderness or lumpiness. If you experience significant changes or discomfort, consult your doctor.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Understanding the tail of Spence is paramount for proactive breast health management. This comprehensive guide has explored its anatomy, common conditions, and the importance of regular self-exams and clinical evaluations. By staying informed and vigilant, you can empower yourself to detect abnormalities early and seek timely medical attention. Early detection significantly improves outcomes for breast-related conditions. Remember, proactive breast health is a lifelong commitment.
The future of breast health lies in personalized approaches and advanced screening technologies. Continue to stay informed about the latest advancements and consult with your healthcare provider about the best screening strategies for you. Share your experiences with breast self-exams and awareness in the comments below to foster a supportive community and promote early detection. Explore our advanced guide to breast cancer prevention for more in-depth information. Contact our experts for a consultation on personalized breast health strategies tailored to your individual needs and risk factors.
