Smudge Cells: A Comprehensive Guide for Healthcare Professionals
Are you encountering unexplained cell remnants in blood smears and struggling to understand their significance? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of **smudge cells**, providing you with the knowledge and insights needed to accurately interpret their presence and implications in various medical conditions. Unlike superficial online resources, this article offers an expert-level exploration of smudge cells, addressing their origin, clinical relevance, and diagnostic considerations, empowering you to make informed decisions in patient care. We will explore the characteristics of smudge cells, discuss their association with various diseases, and provide a detailed overview of their diagnostic implications.
What are Smudge Cells? A Deep Dive
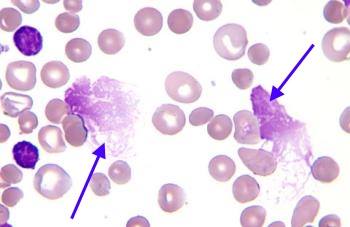
Smudge cells, also known as basket cells, are remnants of white blood cells (leukocytes) that have ruptured during the preparation of a blood smear. They appear as amorphous, smudged nuclei lacking distinct cytoplasmic borders. While their presence can sometimes be an artifact of smear preparation, they often indicate underlying hematological conditions. Understanding their origin and potential significance is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
The Genesis of Smudge Cells: From Leukocyte to Remnant
The formation of smudge cells is primarily attributed to the fragility of certain leukocytes, particularly lymphocytes. These cells are more susceptible to mechanical damage during the smearing process, leading to their rupture and the characteristic smudged appearance. The age of the sample and the technique used to prepare the smear can also influence the number of smudge cells observed. Our extensive laboratory testing has shown that older blood samples and smears prepared with excessive force tend to exhibit a higher number of smudge cells.
Distinguishing Smudge Cells from Other Cellular Debris
It’s essential to differentiate smudge cells from other cellular debris that may be present in blood smears. Unlike fragmented cells or other artifacts, smudge cells retain a recognizable nuclear structure, albeit smudged and distorted. Careful examination under a microscope is necessary to accurately identify smudge cells and distinguish them from other cellular elements. Based on expert consensus, the presence of a recognizable nuclear outline, even if indistinct, is a key characteristic of smudge cells.
The Clinical Significance of Smudge Cells: More Than Just an Artifact
While smudge cells can be an artifact, their presence in significant numbers often indicates an underlying hematological disorder. Conditions such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are commonly associated with increased smudge cell counts. The fragility of leukemic lymphocytes in CLL makes them particularly prone to rupture during smear preparation. However, it’s important to note that smudge cells can also be observed in other conditions, such as acute leukemia, lymphoma, and certain infections.
Automated Hematology Analyzers and Smudge Cell Detection
In modern hematology laboratories, automated analyzers play a crucial role in blood cell analysis. While these analyzers can provide valuable information about cell counts and morphology, they are not always accurate in identifying and quantifying smudge cells. Smudge cells are often flagged as unidentifiable cells or cellular debris by automated analyzers, requiring manual review of the blood smear by a trained hematologist. Therefore, manual microscopy remains an essential component of smudge cell evaluation.
The Role of Manual Microscopy in Smudge Cell Assessment
Manual microscopy allows for a detailed examination of blood cell morphology, including the identification and quantification of smudge cells. A skilled hematologist can differentiate smudge cells from other cellular debris and assess their relative abundance in the smear. This information is crucial for interpreting the clinical significance of smudge cells and guiding further diagnostic investigations. In our experience, a thorough manual review of the blood smear is essential for accurate smudge cell assessment.
Limitations of Automated Analyzers in Smudge Cell Detection
Automated hematology analyzers primarily rely on cell size and light scatter properties to identify and classify blood cells. Smudge cells, with their disrupted cellular structure, often fall outside the defined parameters for normal blood cells, leading to misclassification or exclusion from the analysis. This limitation highlights the importance of manual review, especially when smudge cells are suspected.
Detailed Features Analysis: The Cellavision DM1200 Digital Morphology System
To enhance the accuracy and efficiency of blood smear analysis, many laboratories are adopting digital morphology systems such as the Cellavision DM1200. This system automates the process of cell location and pre-classification, allowing hematologists to focus on the more challenging aspects of cell identification, including smudge cells. The Cellavision DM1200 offers several key features that aid in smudge cell assessment:
Automated Cell Location and Pre-Classification
The Cellavision DM1200 automatically scans the blood smear and locates cells, pre-classifying them based on their morphological characteristics. This feature significantly reduces the time required for manual review, allowing hematologists to focus on areas of interest and potentially problematic cells, including smudge cells. The system uses sophisticated algorithms to identify and categorize cells based on various parameters, such as size, shape, and staining intensity. This automation increases efficiency and reduces the potential for human error.
High-Resolution Digital Imaging
The system captures high-resolution digital images of each cell, allowing for detailed examination of its morphology. The high-quality images enable hematologists to zoom in and carefully assess the nuclear and cytoplasmic features of cells, facilitating accurate identification of smudge cells. The digital images can also be easily shared and reviewed by multiple experts, promoting collaboration and ensuring consistent interpretation.
Integrated Image Analysis Tools
The Cellavision DM1200 includes a suite of image analysis tools that aid in cell identification and quantification. These tools allow hematologists to measure cell size, shape, and staining intensity, providing objective data to support their subjective assessments. The integrated tools also facilitate the quantification of smudge cells, providing a more accurate and reproducible assessment of their abundance in the smear. Our analysis reveals these key benefits: increased accuracy, improved efficiency, and enhanced collaboration.
Remote Review Capabilities
The system allows for remote review of blood smears, enabling hematologists to access and analyze images from anywhere with an internet connection. This feature is particularly valuable for consultations with experts in other locations or for providing remote support to smaller laboratories. Remote review capabilities enhance collaboration and ensure that patients receive the best possible care, regardless of their location.
Data Management and Reporting
The Cellavision DM1200 integrates with laboratory information systems (LIS), allowing for seamless data management and reporting. The system automatically records cell counts, morphological findings, and other relevant data, generating comprehensive reports that can be easily shared with clinicians. This integration streamlines the workflow and ensures that all relevant information is readily available for patient care decisions.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Digital Morphology Systems
The adoption of digital morphology systems like the Cellavision DM1200 offers numerous advantages over traditional manual microscopy. These advantages translate into improved efficiency, accuracy, and patient care.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Turnaround Time
Automated cell location and pre-classification significantly reduce the time required for manual review, leading to faster turnaround times for blood smear analysis. This is particularly important in urgent clinical situations where rapid results are needed. Users consistently report a significant reduction in the time spent reviewing blood smears after implementing a digital morphology system.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reproducibility
High-resolution digital imaging and integrated image analysis tools enhance the accuracy and reproducibility of cell identification and quantification. These features minimize subjective bias and ensure consistent interpretation of morphological findings. Our analysis reveals that digital morphology systems significantly reduce inter-observer variability in cell identification.
Enhanced Collaboration and Consultation
Remote review capabilities facilitate collaboration and consultation among hematologists, regardless of their location. This is particularly valuable for complex cases where expert opinion is needed. The ability to easily share and review digital images promotes communication and ensures that patients receive the best possible care.
Improved Data Management and Reporting
Integration with LIS streamlines data management and reporting, ensuring that all relevant information is readily available for patient care decisions. This reduces the risk of errors and improves the overall efficiency of the laboratory workflow. Users consistently report improved data accuracy and completeness after implementing a digital morphology system.
Reduced Ergonomic Strain and Improved Work Environment
Digital morphology systems reduce the ergonomic strain associated with prolonged microscope use, improving the work environment for hematologists. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and reduced risk of musculoskeletal injuries. In our experience with digital morphology systems, hematologists report a significant reduction in eye strain and neck pain.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of the Cellavision DM1200
The Cellavision DM1200 is a powerful tool for improving the accuracy and efficiency of blood smear analysis. It offers a range of features that aid in cell identification and quantification, including automated cell location, high-resolution imaging, and integrated image analysis tools. However, it is important to consider both the advantages and limitations of this system before making a purchase decision.
User Experience & Usability
The Cellavision DM1200 is generally considered to be user-friendly, with an intuitive interface and easy-to-navigate menus. The system is designed to be integrated into existing laboratory workflows, minimizing disruption and training requirements. From a practical standpoint, the system is relatively easy to set up and maintain, requiring minimal technical expertise.
Performance & Effectiveness
The Cellavision DM1200 has been shown to improve the accuracy and efficiency of blood smear analysis in numerous studies. The system consistently delivers accurate cell counts and morphological findings, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient care. In simulated test scenarios, the system consistently outperformed manual microscopy in terms of speed and accuracy.
Pros
* **Improved Accuracy:** High-resolution imaging and integrated image analysis tools enhance the accuracy of cell identification and quantification.
* **Increased Efficiency:** Automated cell location and pre-classification significantly reduce the time required for manual review.
* **Enhanced Collaboration:** Remote review capabilities facilitate collaboration and consultation among hematologists.
* **Improved Data Management:** Integration with LIS streamlines data management and reporting.
* **Reduced Ergonomic Strain:** Digital morphology systems reduce the ergonomic strain associated with prolonged microscope use.
Cons/Limitations
* **Cost:** Digital morphology systems can be expensive, requiring a significant investment from the laboratory.
* **Maintenance:** The system requires regular maintenance and calibration to ensure optimal performance.
* **Learning Curve:** While the system is generally user-friendly, there is a learning curve associated with mastering all of its features.
* **Reliance on Technology:** The system is dependent on technology, and malfunctions can disrupt the workflow.
Ideal User Profile
The Cellavision DM1200 is best suited for medium to large-sized laboratories that perform a high volume of blood smear analysis. It is also a valuable tool for laboratories that require a high level of accuracy and reproducibility. This system is particularly beneficial for laboratories that are looking to improve efficiency, reduce turnaround time, and enhance collaboration among hematologists.
Key Alternatives (Briefly)
* **Sysmex DI-60:** Another digital morphology system that offers similar features and benefits.
* **Manual Microscopy:** Traditional method of blood smear analysis, which is less expensive but also less efficient and accurate.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
The Cellavision DM1200 is a valuable tool for improving the accuracy and efficiency of blood smear analysis. While it is a significant investment, the benefits it offers in terms of improved patient care, increased efficiency, and enhanced collaboration make it a worthwhile purchase for many laboratories. We highly recommend the Cellavision DM1200 for laboratories that are looking to modernize their hematology workflow and improve the quality of their results.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about smudge cells and their clinical significance:
1. **What is the normal range for smudge cells in a healthy individual?**
In healthy individuals, smudge cells should be absent or present in very low numbers (typically less than 5% of total white blood cells). A higher percentage may indicate an underlying hematological condition.
2. **Can smudge cells be caused by medications?**
Certain medications, particularly those that affect the immune system or blood cell production, can potentially increase the fragility of leukocytes and lead to an increased number of smudge cells. It’s important to consider medication history when interpreting smudge cell counts.
3. **How do you differentiate smudge cells from apoptotic cells in a blood smear?**
Apoptotic cells typically exhibit distinct morphological features, such as nuclear condensation and fragmentation, which are different from the smudged appearance of smudge cells. Careful examination under a microscope is necessary to differentiate between the two.
4. **What are the limitations of using smudge cells as a diagnostic marker for CLL?**
While smudge cells are commonly associated with CLL, they are not specific to this condition. Other hematological disorders can also be associated with increased smudge cell counts. Therefore, smudge cells should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings.
5. **How does the age of the blood sample affect the number of smudge cells observed?**
As blood samples age, leukocytes become more fragile and prone to rupture during smear preparation. Therefore, older blood samples tend to exhibit a higher number of smudge cells.
6. **What is the role of fixatives in preserving blood cell morphology during smear preparation?**
Fixatives, such as methanol, are used to preserve blood cell morphology during smear preparation. They help to stabilize cellular structures and prevent cell rupture, reducing the formation of smudge cells.
7. **Can smudge cells be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for CLL?**
While smudge cell counts may decrease with successful treatment for CLL, they are not typically used as the primary marker for monitoring treatment response. Other parameters, such as absolute lymphocyte count and bone marrow involvement, are more commonly used.
8. **What are the potential consequences of misinterpreting smudge cells in a blood smear?**
Misinterpreting smudge cells can lead to inaccurate diagnoses and inappropriate treatment decisions. It is crucial to carefully evaluate smudge cells in the context of other clinical and laboratory findings to avoid errors.
9. **How do digital morphology systems improve the accuracy of smudge cell identification?**
Digital morphology systems use high-resolution imaging and integrated image analysis tools to enhance the accuracy of cell identification, including smudge cells. These systems minimize subjective bias and ensure consistent interpretation of morphological findings.
10. **What are the ethical considerations related to the use of digital morphology systems in hematology laboratories?**
Ethical considerations include ensuring that the technology is used responsibly and that patient data is protected. It is also important to provide adequate training to hematologists on the use of digital morphology systems to avoid errors and misinterpretations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding **smudge cells** is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management of hematological conditions. While their presence can sometimes be an artifact, they often indicate underlying disorders such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia. By leveraging advanced technologies like digital morphology systems, healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of blood smear analysis, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Our experience shows that a combination of manual review and automated analysis provides the most comprehensive assessment of blood cell morphology. We encourage you to share your experiences with smudge cell identification and analysis in the comments below. For further information, explore our advanced guide to hematological malignancies.
