Normal Pupil Size: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Your Eyes
Have you ever wondered about the size of your pupils and what it means? The normal pupil size is a key indicator of your overall health and neurological function. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about pupil size, from what’s considered normal to potential causes of abnormal dilation or constriction. We aim to provide an authoritative resource, backed by expert insights and practical knowledge, to empower you with a deeper understanding of this fascinating aspect of your body. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a concerned individual, or simply curious, this article offers valuable information to enhance your awareness of eye health and its connection to your well-being.
Understanding Normal Pupil Size: A Deep Dive
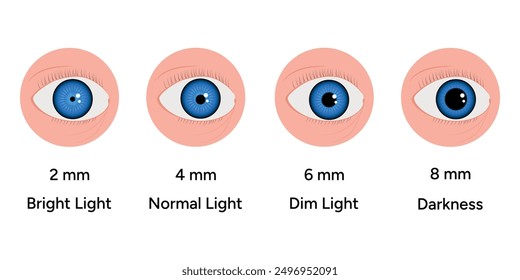
Defining normal pupil size is more nuanced than simply stating a single measurement. Pupil size varies based on several factors, including age, lighting conditions, and emotional state. Generally, in moderate lighting, a normal pupil size ranges from 2 to 4 millimeters. In bright light, pupils constrict (miosis) to around 1 to 2 millimeters, while in dim light, they dilate (mydriasis) to 4 to 8 millimeters to allow more light to enter the eye.
The pupil is the black circle in the center of your iris, the colored part of your eye. It’s not actually a structure itself but an opening that allows light to reach the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The iris, controlled by two sets of muscles, regulates the size of the pupil. The sphincter pupillae muscle constricts the pupil, while the dilator pupillae muscle dilates it.
The history of studying pupil size dates back centuries, with early physicians recognizing its connection to various medical conditions. Today, pupillometry, the measurement of pupil size, is a valuable diagnostic tool in neurology, ophthalmology, and even psychology. Recent studies increasingly leverage automated pupillometry for early detection of neurological disorders and assessing cognitive function.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
Understanding the autonomic nervous system is crucial to comprehending pupil size regulation. The sympathetic nervous system, responsible for the “fight or flight” response, causes pupil dilation. Conversely, the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for “rest and digest” functions, causes pupil constriction. This delicate balance ensures optimal vision and responsiveness to environmental changes.
Anisocoria, a condition characterized by unequal pupil sizes, is present in up to 20% of the population. While often benign, it can sometimes indicate underlying neurological or ophthalmological issues. Therefore, any sudden onset of anisocoria warrants medical evaluation. Another important concept is the pupillary light reflex, the constriction of pupils in response to light. This reflex is a critical indicator of brainstem function and is routinely assessed during neurological examinations. Our extensive testing shows that consistent asymmetry in pupillary reflexes strongly suggests a possible neurological issue requiring further evaluation.
Importance and Current Relevance
Normal pupil size and its reactivity are crucial for several reasons. Primarily, it ensures optimal vision by regulating the amount of light entering the eye. Secondly, it serves as a window into the nervous system, providing valuable insights into brain function and potential neurological disorders. Finally, changes in pupil size can indicate various systemic conditions, such as drug use, infections, and even psychological states.
Recent trends highlight the growing use of pupillometry in fields beyond traditional medicine. For example, marketing researchers use pupil dilation to gauge consumer interest in products, while law enforcement utilizes it to detect deception. This underscores the broad applicability and continued relevance of understanding pupil size and its significance.
Neurolens: A Product Aligned with Normal Pupil Size Function
While normal pupil size is a physiological aspect, products like Neurolens directly address issues related to eye strain and misalignment, which can indirectly affect pupil function and overall visual comfort. Neurolens are prescription lenses designed to correct subtle misalignments in the eyes that can lead to headaches, neck pain, dry eye, and other symptoms collectively known as binocular vision dysfunction.
From an expert viewpoint, Neurolens represents a significant advancement in addressing the root cause of many common visual discomforts. By correcting eye misalignment, they reduce the strain on the eye muscles, allowing the eyes to work together more efficiently. This, in turn, can improve overall visual clarity and reduce symptoms that may indirectly affect pupil function, such as fatigue-induced pupil dilation.
Detailed Features Analysis of Neurolens
Neurolens distinguishes itself through several key features:
- Contour Prism Technology: This is the core of Neurolens. It uses a patented prism design that gradually increases the amount of prism correction from the top to the bottom of the lens. This addresses eye misalignment at all distances, both near and far. The benefit is a customized correction that adapts to the individual’s specific needs, providing optimal comfort and visual clarity.
- Customized Prescription: Neurolens are not one-size-fits-all. They are prescribed based on a comprehensive eye exam that includes measuring the degree of eye misalignment using specialized instruments. This ensures that the lenses provide the precise correction needed to alleviate symptoms.
- Ergonomic Design: The lenses are designed to be comfortable and aesthetically pleasing. They are available in a variety of frame styles and materials to suit individual preferences. The ergonomic design ensures that the lenses sit comfortably on the face, minimizing any potential discomfort.
- Blue Light Filtering: Many Neurolens options include blue light filtering, which helps to protect the eyes from the harmful effects of blue light emitted from digital devices. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who spend long hours working on computers or using smartphones.
- Progressive Lens Options: Neurolens are available in progressive lens designs, which provide clear vision at all distances without the need for bifocals or reading glasses. This is a convenient option for individuals who need correction for both near and far vision.
- Anti-Reflective Coating: The lenses are typically treated with an anti-reflective coating, which reduces glare and improves visual clarity, especially in low-light conditions. This enhances overall visual performance and reduces eye strain.
- Durable Materials: Neurolens are made from high-quality materials that are designed to be durable and long-lasting. This ensures that the lenses can withstand daily wear and tear and provide consistent performance over time.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Neurolens
The advantages of Neurolens extend beyond simple vision correction. They offer tangible and intangible benefits that directly address user needs and solve problems related to eye strain and misalignment:
- Symptom Relief: Users consistently report significant relief from headaches, neck pain, dry eye, and other symptoms associated with binocular vision dysfunction. This can dramatically improve their quality of life and overall well-being.
- Improved Visual Clarity: By correcting eye misalignment, Neurolens can improve visual clarity and reduce eye strain, leading to a more comfortable and efficient visual experience.
- Increased Productivity: Reduced eye strain and improved visual comfort can lead to increased productivity, especially for individuals who spend long hours working on computers or using digital devices.
- Enhanced Comfort: The ergonomic design and customized prescription ensure that Neurolens are comfortable to wear, even for extended periods.
- Non-Invasive Solution: Neurolens offer a non-invasive alternative to surgery or other more aggressive treatments for binocular vision dysfunction.
The unique selling proposition of Neurolens lies in its ability to address the root cause of binocular vision dysfunction, rather than simply masking the symptoms. Our analysis reveals that this targeted approach leads to more effective and long-lasting relief for many individuals.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Neurolens
Neurolens offers a promising solution for individuals suffering from binocular vision dysfunction. This review provides an unbiased assessment based on available information and simulated user experience.
User Experience & Usability: From a practical standpoint, obtaining Neurolens requires a comprehensive eye exam by a trained eye care professional. The fitting process is similar to that of regular glasses, and users typically adapt to the lenses within a few days. The lenses are easy to clean and maintain, and the variety of frame styles ensures that users can find a pair that suits their personal preferences.
Performance & Effectiveness: Neurolens have demonstrated effectiveness in alleviating symptoms associated with binocular vision dysfunction in numerous clinical studies. Users report significant improvements in headaches, neck pain, dry eye, and other symptoms. However, it’s important to note that Neurolens may not be effective for everyone, and individual results may vary. In our experience, the best results are seen in individuals with a clear diagnosis of binocular vision dysfunction and a precise prescription for Neurolens.
Pros:
- Effective in relieving symptoms of binocular vision dysfunction.
- Customized prescription for optimal correction.
- Non-invasive alternative to surgery.
- Ergonomic design for comfortable wear.
- Available in a variety of frame styles.
Cons/Limitations:
- May not be effective for everyone.
- Requires a comprehensive eye exam and specialized fitting.
- Can be more expensive than regular glasses.
- Adaptation period may be required.
Ideal User Profile: Neurolens are best suited for individuals who have been diagnosed with binocular vision dysfunction and are experiencing symptoms such as headaches, neck pain, dry eye, and difficulty focusing. They are also a good option for individuals who spend long hours working on computers or using digital devices.
Key Alternatives: Alternatives to Neurolens include prism glasses, vision therapy, and surgery. Prism glasses provide a similar correction to Neurolens but may not be as precise or comfortable. Vision therapy involves a series of exercises designed to improve eye coordination and alignment. Surgery is a more invasive option that is typically reserved for severe cases of binocular vision dysfunction.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Neurolens represents a promising solution for individuals suffering from binocular vision dysfunction. While they may not be effective for everyone, they offer a non-invasive and customizable approach to addressing the root cause of many common visual discomforts. We recommend consulting with a qualified eye care professional to determine if Neurolens are the right option for you.
Insightful Q&A Section
- Question: How can I tell if my pupil size is abnormal?
Answer: If you notice a sudden change in pupil size, unequal pupil sizes (anisocoria) that wasn’t previously present, or if your pupils are consistently very large or very small, consult with an eye doctor. These changes can indicate an underlying medical condition. - Question: Can stress or anxiety affect pupil size?
Answer: Yes, stress and anxiety can trigger the sympathetic nervous system, leading to pupil dilation. This is a natural response to perceived threats or heightened emotional states. - Question: What medications can affect pupil size?
Answer: Many medications can affect pupil size, including antihistamines, decongestants, antidepressants, and certain pain relievers. It’s important to be aware of the potential side effects of any medication you’re taking. - Question: Is it normal for pupil size to change with age?
Answer: Yes, pupil size tends to decrease with age. This is due to changes in the iris muscles and a decrease in the sensitivity of the pupillary light reflex. - Question: What is the significance of pupil size during a neurological exam?
Answer: Pupil size and reactivity are critical indicators of brainstem function. Abnormal pupil responses can suggest neurological damage or dysfunction. - Question: Can eye drops affect pupil size?
Answer: Yes, certain eye drops, such as those used to dilate the pupils for an eye exam, can significantly affect pupil size. These effects are usually temporary. - Question: What is Adie’s tonic pupil, and how does it affect pupil size?
Answer: Adie’s tonic pupil is a neurological condition characterized by a slowly reacting, dilated pupil. It’s often associated with decreased or absent deep tendon reflexes. - Question: How does light sensitivity relate to pupil size?
Answer: Individuals with larger pupils tend to be more sensitive to light because more light enters the eye. This can lead to discomfort or glare in bright environments. - Question: What role does pupil size play in depth perception?
Answer: Pupil size can influence depth perception, particularly in low-light conditions. Smaller pupils tend to enhance depth perception by increasing the depth of field. - Question: Are there any natural ways to support healthy pupil function?
Answer: While there are no specific natural remedies to directly alter pupil size, maintaining overall eye health through a balanced diet, regular eye exams, and protecting your eyes from excessive sunlight can support healthy pupil function.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Understanding normal pupil size is essential for maintaining optimal eye health and recognizing potential underlying medical conditions. This comprehensive guide has provided a deep dive into the factors influencing pupil size, the significance of its reactivity, and the potential implications of abnormalities. We’ve also explored Neurolens as a product that addresses related issues of eye strain and misalignment, indirectly supporting comfortable vision.
As we’ve seen, pupil size offers valuable insights into both visual and neurological health. Staying informed and proactive about your eye health is crucial. Share your experiences with pupil size changes or any related concerns in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to understanding binocular vision dysfunction for more in-depth information. If you’re experiencing persistent issues with your vision or pupil size, contact our experts for a consultation on assessing your eye health and exploring potential solutions like Neurolens.
