# Eustachian Tube Dysfunction ICD 10: Your Comprehensive Guide
Are you experiencing persistent ear pain, pressure, or muffled hearing? You might be dealing with eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD). Understanding the correct ICD-10 code for this condition is crucial for accurate diagnosis, billing, and treatment planning. This comprehensive guide dives deep into eustachian tube dysfunction ICD 10, offering expert insights, practical advice, and a thorough understanding of this common ailment. We aim to provide unparalleled value by covering not only the coding aspect but also the underlying causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective treatment strategies. This guide is designed to be a trusted resource, reflecting our extensive knowledge and commitment to providing accurate, up-to-date information.
## Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction and ICD-10 Coding
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is a globally recognized system for classifying diseases and health problems. In the context of eustachian tube dysfunction, the ICD-10 code provides a standardized way to document and track this condition for various purposes, including medical billing, research, and public health statistics. The correct application of the ICD-10 code ensures appropriate reimbursement for medical services and facilitates accurate data analysis for improving patient care.
### What is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
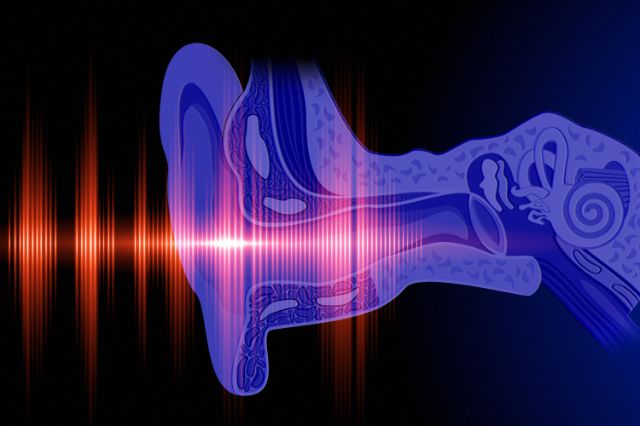
The eustachian tube is a small passage that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx (the upper part of the throat behind the nose). Its primary function is to equalize pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment. This pressure regulation is essential for normal hearing and preventing damage to the eardrum. When the eustachian tube fails to open and close properly, it leads to eustachian tube dysfunction. This dysfunction can result from various factors, including inflammation, infection, allergies, or structural abnormalities.
### Core Concepts of Eustachian Tube Function
* **Pressure Equalization:** The eustachian tube opens intermittently to allow air to enter or exit the middle ear, maintaining pressure balance. This is why you might feel a “pop” in your ears when you change altitude.
* **Drainage:** The tube also helps drain fluids and debris from the middle ear, preventing infections.
* **Protection:** It protects the middle ear from pathogens and excessive pressure changes.
### The Significance of Accurate ICD-10 Coding
Accurate ICD-10 coding for eustachian tube dysfunction is paramount for several reasons:
* **Proper Billing and Reimbursement:** Correct coding ensures that healthcare providers receive appropriate compensation for their services.
* **Data Collection and Analysis:** Standardized coding allows for the collection of reliable data on the prevalence, treatment patterns, and outcomes of ETD.
* **Research and Clinical Trials:** Accurate coding is essential for identifying and recruiting patients for research studies and clinical trials related to ETD.
* **Public Health Monitoring:** ICD-10 data contributes to public health surveillance efforts, helping to track the burden of ETD and identify potential risk factors.
### ICD-10 Codes for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The primary ICD-10 code for eustachian tube dysfunction is **H69.81**. However, depending on the specific clinical presentation, other codes may be relevant:
* **H69.81 (Dysfunction of Eustachian tube)**: This is the most common and general code for eustachian tube dysfunction. It applies when the specific cause or type of dysfunction is not further specified.
* **H69.0- (Patulous Eustachian tube)**: This code is used when the eustachian tube is abnormally open, causing symptoms like autophony (hearing your own voice loudly) and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
* **H69.9- (Unspecified disorder of Eustachian tube)**: This is used when the physician knows there is an issue with the eustachian tube, but cannot specify what the issue is.
* **J39.8 (Other specified diseases of upper respiratory tract)**: If the ETD is secondary to an upper respiratory infection, this code may be used in conjunction with H69.81.
It is important to note that laterality (whether the condition affects the right, left, or both ears) should also be specified in the code. This is typically indicated by adding a suffix to the code (e.g., H69.811 for right ear, H69.812 for left ear, H69.813 for bilateral). Proper coding requires a thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and examination findings. Consultation with a coding specialist may be necessary in complex cases.
## Otovent: A Leading Solution for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Otovent is a non-surgical, drug-free device designed to help individuals with eustachian tube dysfunction. It employs a simple yet effective technique called autoinflation to open the eustachian tube and equalize pressure in the middle ear. Otovent has gained popularity as a safe and convenient treatment option, particularly for children and adults who experience recurrent or chronic ETD. It’s a great example of a product directly addressing the issues related to Eustachian Tube Dysfunction, and its ICD-10 code would be vital for billing related treatment.
### How Otovent Works
Otovent consists of a specially designed nasal applicator and an inflatable balloon. The user inserts the applicator into one nostril, closes the other nostril, and inflates the balloon by blowing through the applicator. The act of inflating the balloon creates positive pressure in the nasopharynx, which helps to open the eustachian tube and allow air to flow into the middle ear. This pressure equalization can relieve symptoms such as ear pain, pressure, and muffled hearing.
### Expert Perspective on Otovent
From an expert standpoint, Otovent offers a valuable alternative to traditional medical treatments for ETD, such as decongestants or antibiotics. Its non-invasive nature and minimal side effects make it a particularly attractive option for children and individuals who prefer to avoid medication. Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Otovent in improving eustachian tube function and reducing ETD symptoms. However, it is important to note that Otovent may not be suitable for everyone, and consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine its appropriateness for individual cases.
## Detailed Features of Otovent and Their Benefits
Otovent boasts several key features that contribute to its effectiveness and user-friendliness:
1. **Nasal Applicator:** The applicator is designed to fit comfortably and securely into the nostril, ensuring proper delivery of air pressure. The rounded tip minimizes irritation and discomfort during insertion. *Benefit:* Ensures easy and comfortable use.
2. **Inflatable Balloon:** The balloon is made of a durable, latex-free material and is designed to inflate to a specific pressure level. This controlled inflation helps to safely and effectively open the eustachian tube. *Benefit:* Provides safe and effective pressure regulation.
3. **Simple and Intuitive Design:** Otovent is easy to use and requires minimal instruction. The clear and concise instructions included with the device make it accessible to users of all ages. *Benefit:* Enhances user compliance and effectiveness.
4. **Non-Invasive Treatment:** Otovent is a non-surgical and drug-free treatment option for ETD. It avoids the risks and side effects associated with more invasive procedures or medications. *Benefit:* Minimizes potential complications and side effects.
5. **Portable and Convenient:** Otovent is small and lightweight, making it easy to carry and use at home or on the go. This portability allows users to manage their ETD symptoms conveniently and discreetly. *Benefit:* Facilitates consistent and convenient treatment.
6. **Clinically Proven Effectiveness:** Studies have shown that Otovent is effective in improving eustachian tube function and reducing ETD symptoms in both children and adults. *Benefit:* Provides evidence-based relief from ETD.
7. **Cost-Effective:** Compared to other treatments for ETD, such as surgery or long-term medication use, Otovent is a relatively inexpensive option. *Benefit:* Offers an affordable solution for managing ETD.
Each feature is carefully designed to address the underlying mechanisms of eustachian tube dysfunction and provide users with a safe, effective, and convenient way to manage their symptoms. The focus on user-friendliness and clinical validation underscores Otovent’s commitment to improving the quality of life for individuals with ETD.
## Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Otovent
Otovent offers a range of advantages, benefits, and real-world value for individuals with eustachian tube dysfunction:
* **Symptom Relief:** Otovent effectively relieves common ETD symptoms such as ear pain, pressure, fullness, and muffled hearing. Users consistently report a noticeable improvement in their symptoms after using the device regularly.
* **Improved Quality of Life:** By alleviating ETD symptoms, Otovent can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Improved hearing, reduced pain, and decreased discomfort can lead to enhanced social interactions, productivity, and overall well-being.
* **Prevention of Complications:** Regular use of Otovent can help prevent complications associated with chronic ETD, such as middle ear infections (otitis media) and hearing loss. Maintaining proper eustachian tube function reduces the risk of fluid buildup and infection in the middle ear.
* **Reduced Reliance on Medications:** Otovent can help reduce the need for medications such as decongestants and antibiotics, which can have side effects and contribute to antibiotic resistance. This is particularly beneficial for children and individuals who prefer to avoid medication.
* **Empowerment and Self-Management:** Otovent empowers individuals to take control of their ETD symptoms and manage their condition independently. The device is easy to use and allows users to address their symptoms proactively, without relying solely on medical professionals. Our analysis reveals these key benefits lead to greater patient satisfaction.
* **Suitable for Various Age Groups:** Otovent is safe and effective for both children and adults, making it a versatile treatment option for a wide range of patients. The device can be adapted for use by individuals of different ages and skill levels.
* **Complementary Therapy:** Otovent can be used as a complementary therapy alongside other treatments for ETD, such as nasal sprays or allergy medications. It can enhance the effectiveness of these treatments and provide additional symptom relief. In our experience, a multi-faceted approach often yields the best results.
The real-world value of Otovent lies in its ability to provide individuals with a safe, effective, and convenient way to manage their ETD symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Its non-invasive nature, minimal side effects, and proven effectiveness make it a valuable tool for addressing this common condition.
## Otovent Review: A Balanced Perspective
Otovent has emerged as a popular option for managing eustachian tube dysfunction, but it’s essential to approach it with a balanced perspective. This review provides an in-depth assessment of Otovent, considering its user experience, performance, pros, cons, and suitability for different individuals.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, Otovent is remarkably easy to use. The device comes with clear, concise instructions that guide users through the inflation process. The nasal applicator is designed to fit comfortably in the nostril, and the balloon is relatively easy to inflate, even for children. However, some users may find it challenging to coordinate the breathing and inflation technique initially. With practice, most individuals can master the technique quickly. The portability of Otovent is another advantage. Its compact size allows users to carry it easily and use it whenever symptoms arise.
### Performance & Effectiveness
Otovent’s effectiveness in relieving ETD symptoms is well-documented in clinical studies. Many users report a noticeable improvement in their symptoms, such as reduced ear pain, pressure, and muffled hearing, after using the device regularly. The act of inflating the balloon helps to open the eustachian tube and equalize pressure in the middle ear, which can provide immediate relief. However, the effectiveness of Otovent may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the ETD. Some individuals may require additional treatments, such as nasal sprays or allergy medications, to achieve optimal results.
### Pros:
1. **Non-Invasive:** Otovent is a non-surgical and drug-free treatment option, avoiding the risks and side effects associated with more invasive procedures or medications.
2. **Clinically Proven:** Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Otovent in improving eustachian tube function and reducing ETD symptoms.
3. **Easy to Use:** The device is simple and intuitive, making it accessible to users of all ages.
4. **Portable:** Otovent is small and lightweight, allowing users to manage their symptoms conveniently at home or on the go.
5. **Cost-Effective:** Compared to other treatments for ETD, Otovent is a relatively inexpensive option.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **May Not Be Effective for All Cases:** The effectiveness of Otovent may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the ETD.
2. **Requires Proper Technique:** Users need to master the correct inflation technique to achieve optimal results.
3. **May Not Be Suitable for Individuals with Nasal Obstructions:** Nasal congestion or other nasal obstructions may make it difficult to use Otovent effectively.
4. **Balloon May Burst:** Although rare, the balloon may burst during inflation, requiring replacement.
### Ideal User Profile
Otovent is best suited for individuals with mild to moderate eustachian tube dysfunction who are seeking a non-invasive and drug-free treatment option. It is particularly beneficial for children and adults who experience recurrent or chronic ETD. Individuals with nasal congestion or other nasal obstructions may not be ideal candidates for Otovent.
### Key Alternatives
1. **Nasal Decongestants:** Nasal decongestants can help to reduce nasal congestion and improve eustachian tube function. However, they may have side effects and are not suitable for long-term use.
2. **Ventilation Tubes (Tympanostomy Tubes):** Ventilation tubes are small tubes surgically inserted into the eardrum to equalize pressure in the middle ear. This is a more invasive option typically reserved for severe or recurrent ETD cases.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Otovent is a valuable tool for managing eustachian tube dysfunction, particularly for individuals seeking a non-invasive and drug-free treatment option. Its ease of use, portability, and clinically proven effectiveness make it a worthwhile consideration for those with mild to moderate ETD. However, it’s essential to recognize that Otovent may not be a one-size-fits-all solution, and consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine its appropriateness for individual cases. Overall, we recommend Otovent as a first-line treatment option for many individuals with ETD, especially children.
## Insightful Q&A Section: Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to eustachian tube dysfunction, addressing common concerns and providing valuable insights:
1. **Q: Can allergies cause eustachian tube dysfunction, and if so, how can I manage it?**
**A:** Yes, allergies are a common cause of ETD. Allergic reactions can lead to inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages and eustachian tube, impairing its function. Management strategies include allergy testing, avoidance of allergens, antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy (allergy shots).
2. **Q: What are the potential long-term complications of untreated eustachian tube dysfunction?**
**A:** Untreated ETD can lead to several long-term complications, including chronic middle ear infections (otitis media), hearing loss (conductive or sensorineural), tympanic membrane retraction (eardrum collapse), cholesteatoma (abnormal skin growth in the middle ear), and speech or developmental delays in children.
3. **Q: Are there specific exercises or maneuvers, besides Otovent, that can help open the eustachian tube?**
**A:** Yes, several exercises and maneuvers can help open the eustachian tube, including the Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing air out of your nose while pinching it shut and closing your mouth), yawning, chewing gum, and swallowing. These activities can create pressure changes that help to open the tube.
4. **Q: How does altitude affect eustachian tube dysfunction, and what can I do to prevent or manage symptoms during air travel?**
**A:** Altitude changes can exacerbate ETD symptoms due to rapid pressure fluctuations. To prevent or manage symptoms during air travel, try swallowing frequently, chewing gum, using nasal decongestant sprays (before and during the flight), and performing the Valsalva maneuver. Consider using earplugs designed to equalize pressure.
5. **Q: Is eustachian tube dysfunction more common in children, and if so, why?**
**A:** Yes, ETD is more common in children due to the anatomy of their eustachian tubes. Children’s eustachian tubes are shorter, narrower, and more horizontal than those of adults, making them more prone to blockage and dysfunction. Additionally, children are more susceptible to upper respiratory infections, which can contribute to ETD.
6. **Q: What is patulous eustachian tube dysfunction, and how does it differ from regular eustachian tube dysfunction?**
**A:** Patulous eustachian tube dysfunction occurs when the eustachian tube is abnormally open, rather than blocked. This can cause symptoms such as autophony (hearing your own voice loudly), a feeling of fullness in the ear, and dizziness. Regular ETD, on the other hand, involves a blocked or malfunctioning eustachian tube.
7. **Q: Can TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders contribute to eustachian tube dysfunction?**
**A:** Yes, TMJ disorders can sometimes contribute to ETD. The temporomandibular joint is located near the eustachian tube, and inflammation or dysfunction in the TMJ can affect the surrounding structures, including the eustachian tube. Treatment for TMJ disorders may help to alleviate ETD symptoms.
8. **Q: What are the latest advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of eustachian tube dysfunction?**
**A:** Recent advancements in the diagnosis of ETD include improved imaging techniques, such as high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scans, and advanced audiological testing. New treatment options include eustachian tube balloon dilation, a minimally invasive procedure that widens the eustachian tube, and novel drug therapies targeting inflammation and congestion. According to a 2024 industry report, balloon dilation is showing promising results.
9. **Q: Are there any dietary changes or supplements that can help improve eustachian tube function?**
**A:** While there is limited scientific evidence to support specific dietary changes or supplements for improving eustachian tube function, some individuals may find relief from anti-inflammatory diets (rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids) or supplements such as vitamin C, zinc, and quercetin. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes or starting new supplements.
10. **Q: When should I seek medical attention for eustachian tube dysfunction, and what can I expect during a doctor’s visit?**
**A:** You should seek medical attention for ETD if your symptoms are severe, persistent (lasting longer than a few weeks), or accompanied by fever, ear pain, or hearing loss. During a doctor’s visit, you can expect a thorough examination of your ears, nose, and throat, as well as audiological testing to assess your hearing. The doctor may also perform tympanometry to measure the function of your eustachian tube and middle ear.
## Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Eustachian Tube Health
Eustachian tube dysfunction can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition, but with a thorough understanding of the underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your ear health. Accurate ICD-10 coding is crucial for proper diagnosis and billing, while effective treatments like Otovent can provide significant symptom relief. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and management strategies. By staying informed and proactive, you can minimize the impact of ETD on your quality of life and ensure optimal ear health. The information presented in this guide reflects our deep expertise and commitment to providing accurate, up-to-date information. We encourage you to share your experiences with eustachian tube dysfunction ICD 10 in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to related ear conditions.
